Dosing & Drug Interactions
Dosing WAKIX With Other Medications
Some medications have clinically important drug interactions with WAKIX
Choose from the drop-down menu or from the drug categories below.
This tool is not intended to provide an exhaustive list of drug interactions with WAKIX, and some drugs may have other interactions and/or safety considerations. Before prescribing, always consult the Full Prescribing Information for WAKIX as well as for concomitant medications.
Concomitant administration of WAKIX with strong CYP2D6 inhibitors increases WAKIX exposure by 2.2-fold
Dosage modifications for WAKIX are recommended with concomitant use with strong CYP2D6 inhibitors
- Bupropion, Paroxetine
Initiating WAKIX in Adult Patients Currently Receiving Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors
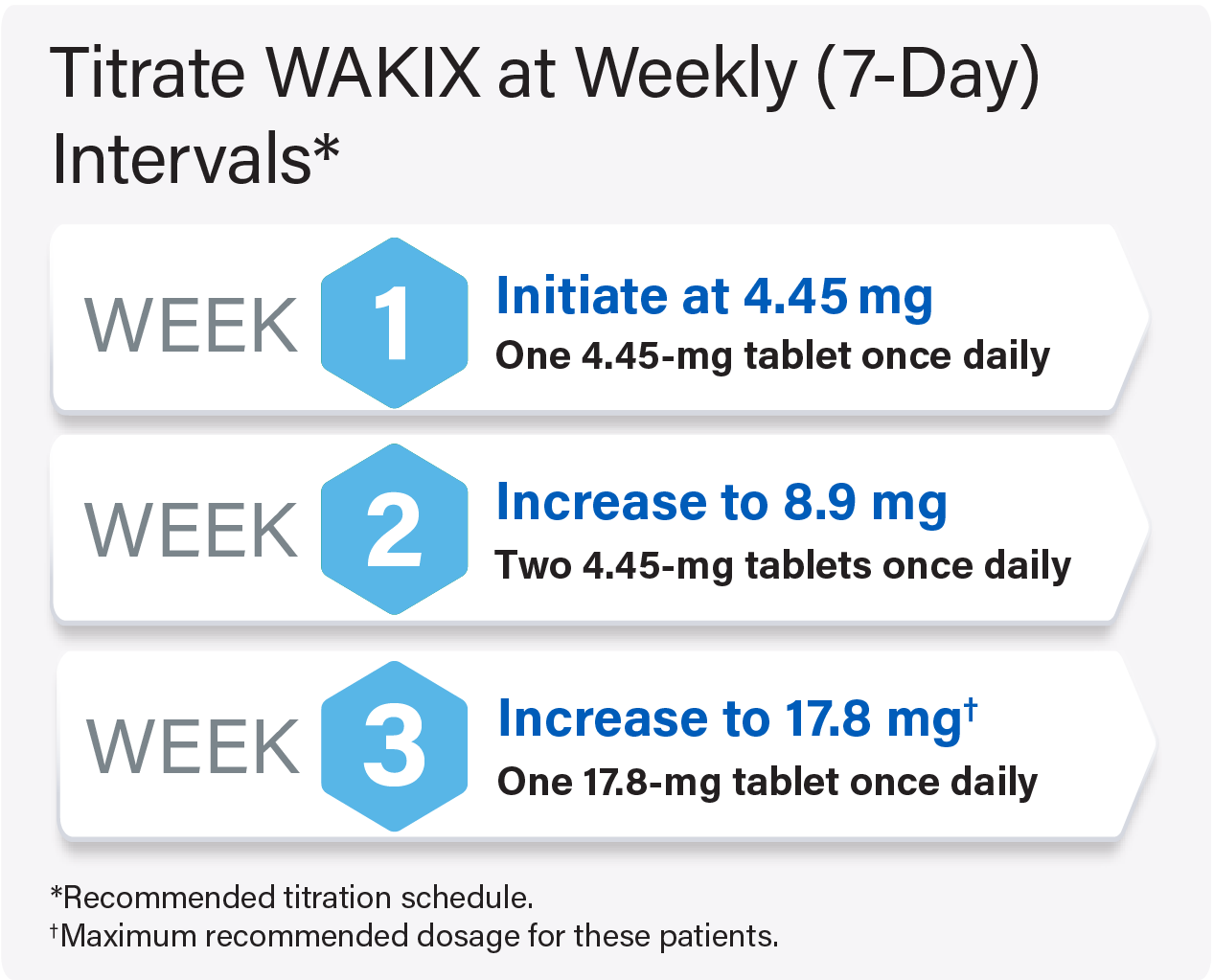
Titrate WAKIX to a maximum recommended dosage of 17.8 mg once daily

Initiating WAKIX in Pediatric Patients (6 Years and Older) Currently Receiving Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors
For pediatric patients weighing <40 kg: Titrate WAKIX to a maximum recommended dosage of 8.9 mg once daily
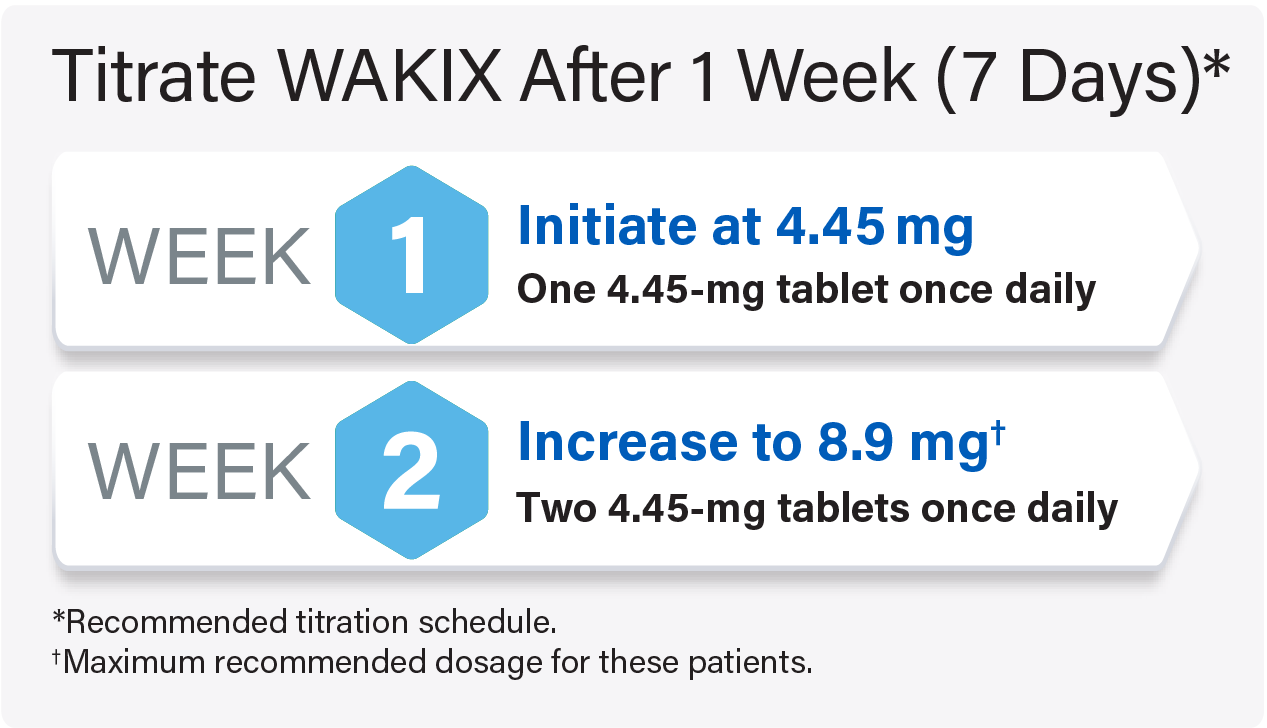
For pediatric patients weighing ≥40 kg: Titrate WAKIX to a maximum recommended dosage of 17.8 mg once daily
Initiating Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors in Patients on a Stable Dose of WAKIX
For adult and pediatric patients on a stable dose of WAKIX: Reduce the WAKIX dose by half upon initiating strong CYP2D6 inhibitors
Concomitant use of WAKIX with strong CYP3A4 inducers decreases WAKIX exposure by 50%
Dosage modifications for WAKIX may be required with concomitant use with strong CYP3A4 inducers
- Carbamazepine, Phenytoin, Rifampin
Initiating Strong CYP3A4 Inducers in Patients on a Stable Dose of WAKIX
Assess for loss of efficacy of WAKIX after initiation of a strong CYP3A4 inducer
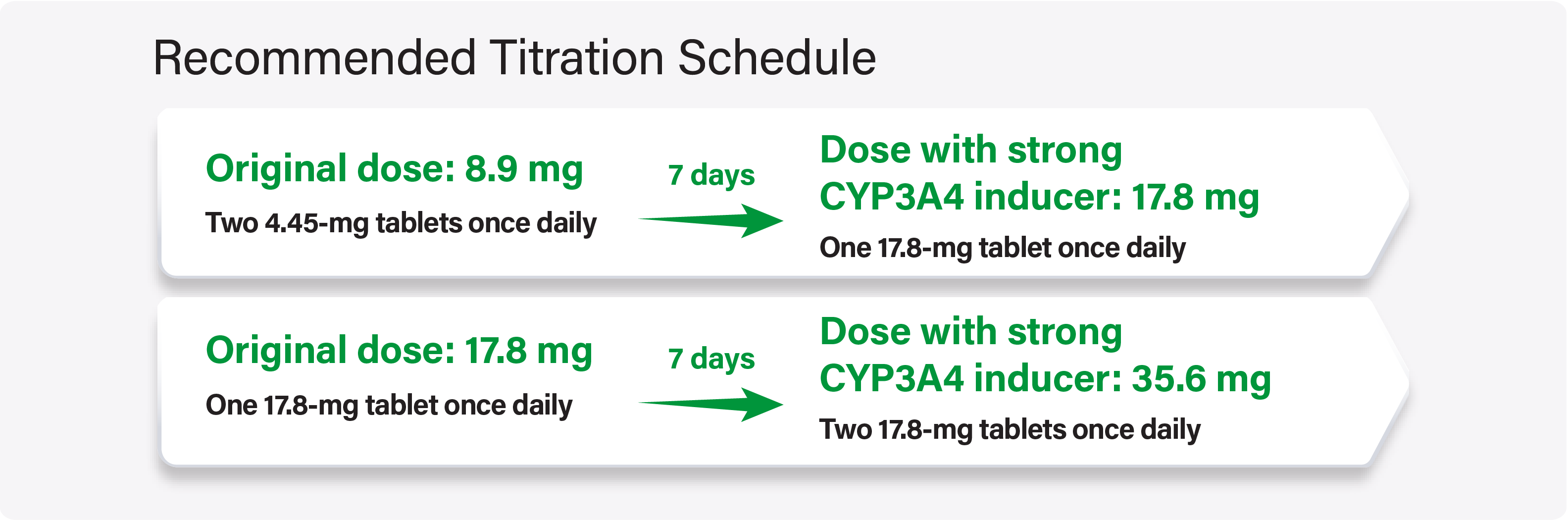
For adult and pediatric patients stable on WAKIX 8.9 mg or 17.8 mg once daily, increase the dose of WAKIX to double the original daily dose over 7 days
Discontinuing Concomitant Strong CYP3A4 Inducers in Patients on a Stable Dose of WAKIX
If concomitant dosing of a strong CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued, decrease WAKIX dosage by half
- Certain antihistamines2: Diphenhydramine, Pheniramine maleate, Promethazine
- Certain tri- or tetracyclic antidepressants: Clomipramine,3 Imipramine,3 Mirtazapine3,4

Concomitant use of WAKIX with centrally acting histamine 1 (H1) receptor antagonists may reduce the effectiveness of WAKIX
Avoid use of centrally acting H1 receptor antagonists
- Class 1A antiarrhythmics: Disopyramide, Procainamide, Quinidine
- Class 3 antiarrhythmics: Amiodarone, Sotalol
- Certain antipsychotics: Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine, Ziprasidone
- Certain antibiotics: Moxifloxacin

Concomitant use of WAKIX with drugs that prolong the QT interval may add to the QT effects of WAKIX and increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmia
Avoid use of WAKIX in combination with other drugs known to prolong the QT interval
- Cyclosporine,6 Hormonal contraceptives, Midazolam1

Concomitant use of WAKIX with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates may reduce the effectiveness of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates
The effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives may be reduced during treatment with WAKIX and for 21 days after discontinuing therapy
Patients using hormonal contraception should be advised to use an alternative non-hormonal contraceptive method during treatment with WAKIX and for at least 21 days after discontinuation of WAKIX
Concomitant administration of WAKIX with strong CYP2D6 inhibitors increases WAKIX exposure by 2.2-fold
Dosage modifications for WAKIX are recommended with concomitant use with strong CYP2D6 inhibitors
Bupropion, Paroxetine
Initiating WAKIX in Adult Patients Currently Receiving Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors
Titrate WAKIX to a maximum recommended dosage of 17.8 mg once daily

Initiating WAKIX in Pediatric Patients (6 Years and Older) Currently Receiving Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors
For pediatric patients weighing <40 kg: Titrate WAKIX to a maximum recommended dosage of 8.9 mg once daily
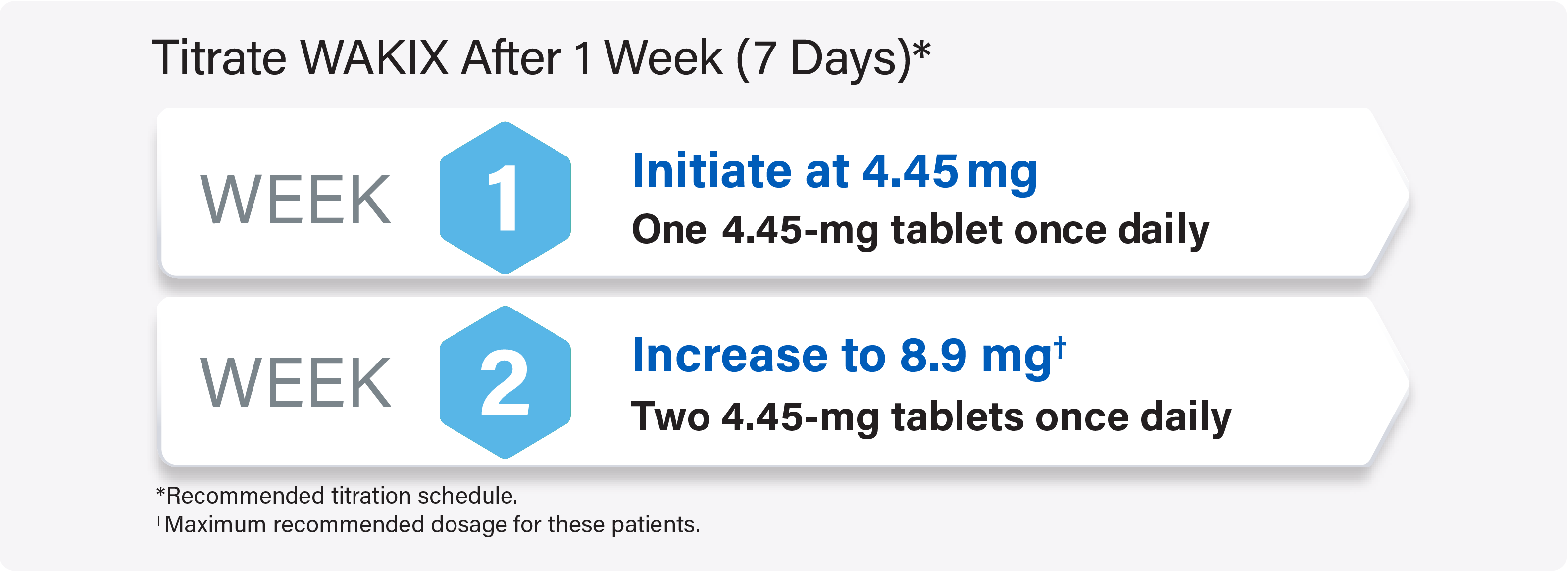
For pediatric patients weighing ≥40 kg: Titrate WAKIX to a maximum recommended dosage of 17.8 mg once daily
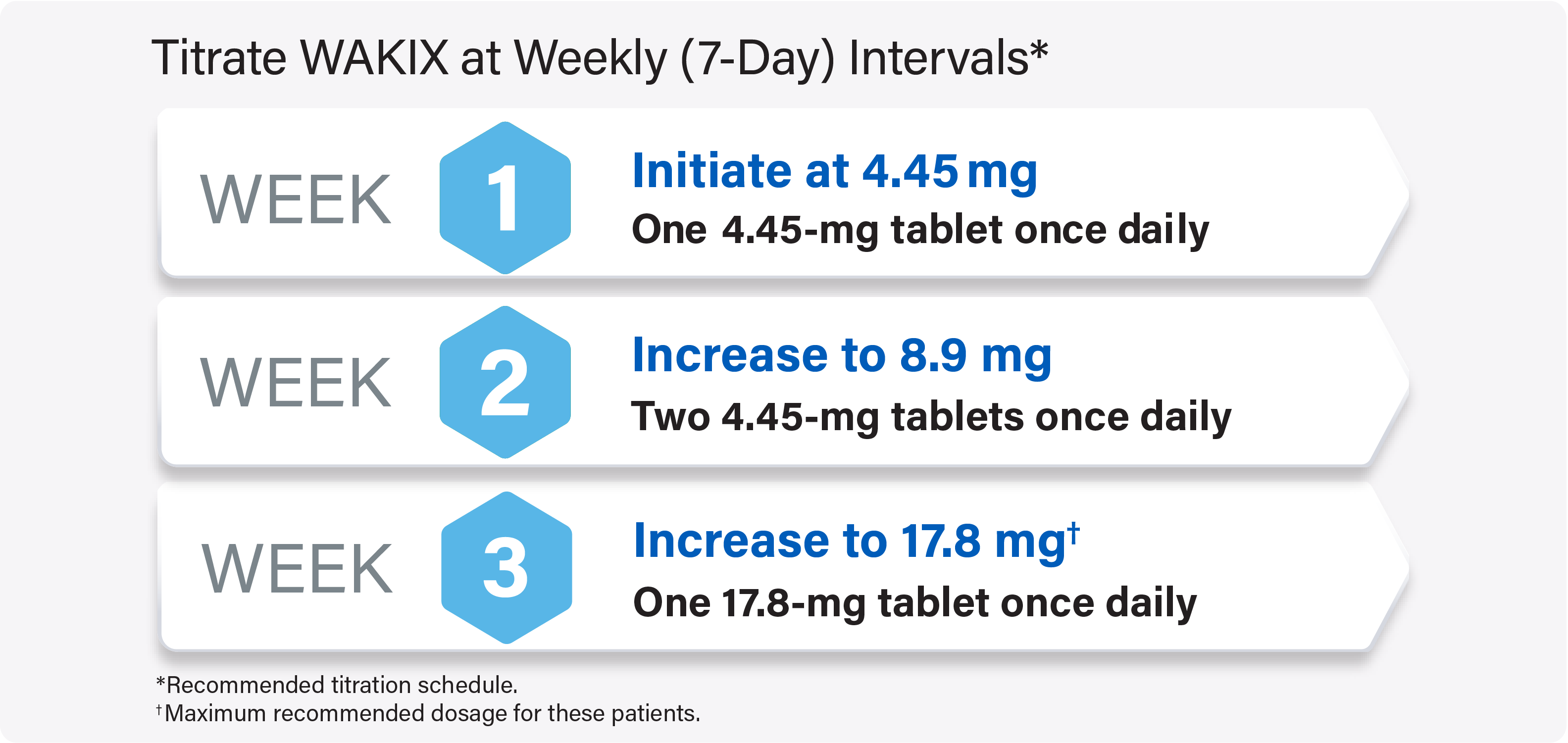
Initiating Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors in Patients on a Stable Dose of WAKIX
For adult and pediatric patients on a stable dose of WAKIX: Reduce the WAKIX dose by half upon initiating strong CYP2D6 inhibitors
Concomitant use of WAKIX with strong CYP3A4 inducers decreases WAKIX exposure by 50%
Dosage modifications for WAKIX may be required with concomitant use with strong CYP3A4 inducers
Carbamazepine, Phenytoin, Rifampin
Initiating Strong CYP3A4 Inducers in Patients on a Stable Dose of WAKIX
Assess for loss of efficacy of WAKIX after initiation of a strong CYP3A4 inducer
For adult and pediatric patients stable on WAKIX 8.9 mg or 17.8 mg once daily, increase the dose of WAKIX to double the original daily dose over 7 days

Discontinuing Concomitant Strong CYP3A4 Inducers in Patients on a Stable Dose of WAKIX
If concomitant dosing of a strong CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued, decrease WAKIX dosage by half
Certain antihistamines2: Diphenhydramine, Pheniramine maleate, Promethazine
Certain tri- or tetracyclic antidepressants: Clomipramine,3 Imipramine,3 Mirtazapine3,4

Concomitant use of WAKIX with centrally acting histamine 1 (H1) receptor antagonists may reduce the effectiveness of WAKIX
Avoid use of centrally acting H1 receptor antagonists
Class 1A antiarrhythmics: Disopyramide, Procainamide, Quinidine
Class 3 antiarrhythmics: Amiodarone, Sotalol
Certain antipsychotics: Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine, Ziprasidone
Certain antibiotics: Moxifloxacin

Concomitant use of WAKIX with drugs that prolong the QT interval may add to the QT effects of WAKIX and increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmia
Avoid use of WAKIX in combination with other drugs known to prolong the QT interval
Cyclosporine,6 Hormonal contraceptives, Midazolam1
